In the contemporary financial landscape, trading platforms have become essential tools for investors and traders seeking to participate in various markets. Despite differences in branding and specific features, many trading platforms operate on fundamentally similar principles that enable users to buy and sell financial instruments efficiently. Understanding how these platforms function can provide insight into their widespread adoption and the seamless user experience they offer.
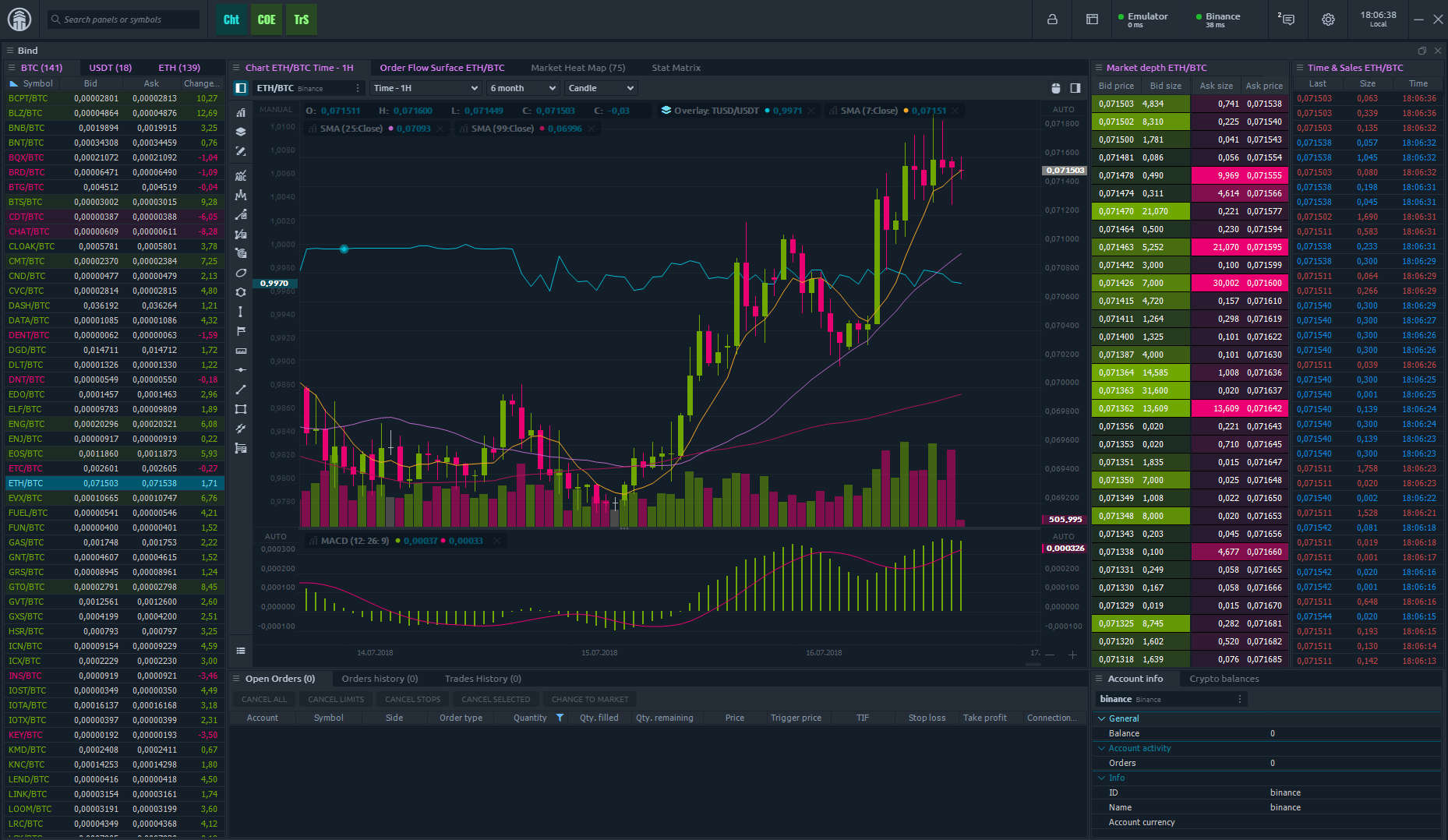
At their core, trading platforms serve as intermediaries between market participants and financial exchanges. They provide a digital interface through which users can access real-time market data, place orders, monitor portfolios, and execute trades across different asset classes such as stocks, commodities, currencies, or cryptocurrencies. These platforms typically connect to one or multiple exchanges via electronic communication networks (ECNs), ensuring that trade orders are routed promptly to the appropriate marketplace for execution.
One of the key operational aspects of these platforms is order management. When a trader submits an order-whether it’s a market order to buy or sell immediately at the best available price or a limit order specifying a particular price-the platform processes this request by validating account details such as available funds or margin requirements. Once validated, the order is transmitted electronically to an exchange where it is matched with corresponding buy or sell orders from other market participants. The speed of this process is crucial; most modern platforms leverage advanced technology infrastructure capable of executing trades within milliseconds.
Another common feature shared by similar trading systems is real-time data streaming. Users rely heavily on up-to-the-second information regarding prices, volumes, bid-ask spreads, and news events that could impact markets. Trading platforms aggregate data feeds from exchanges and third-party providers to present comprehensive dashboards displaying charts, technical indicators, and analytics tools designed for informed decision-making.
Risk management functionalities also play an integral role in platform operations. Many allow users to set stop-loss orders or take-profit levels automatically triggering trade closures when certain conditions are met-helping mitigate potential losses without constant manual monitoring. Additionally, margin accounts offered by some brokers enable leveraged trading but require continuous tracking of equity levels through margin calls integrated into platform alerts.
Security measures underpinning these systems are stringent due to the sensitive nature of financial transactions involved. Platforms employ encryption protocols for data transmission alongside multi-factor authentication methods aimed at preventing unauthorized access while safeguarding user assets.
In summary, despite variations in design aesthetics or additional services provided by individual companies offering them, how similar platforms operate based on established mechanisms involving efficient order routing through ECNs connected with exchanges; real-time market data delivery; risk management tools; secure transaction processing; all orchestrated via sophisticated technological frameworks ensuring speed and reliability necessary for active trading environments worldwide.